What is TPE? - Featured 3
ktpe_summary
- TPE combine the dynamic processing properties of thermoplastic plastics with the softness and flexibility of elastomers.
- TPE materials classify them as belonging to a group of materials between thermoplastics and elastomers.
- TPEs are produced and delivered to the customer in pellet form. The granules from KRAIBURG TPE can be processed without the addition of other substances.
- TPEs are heated to process them by means of injection molding or extrusion.
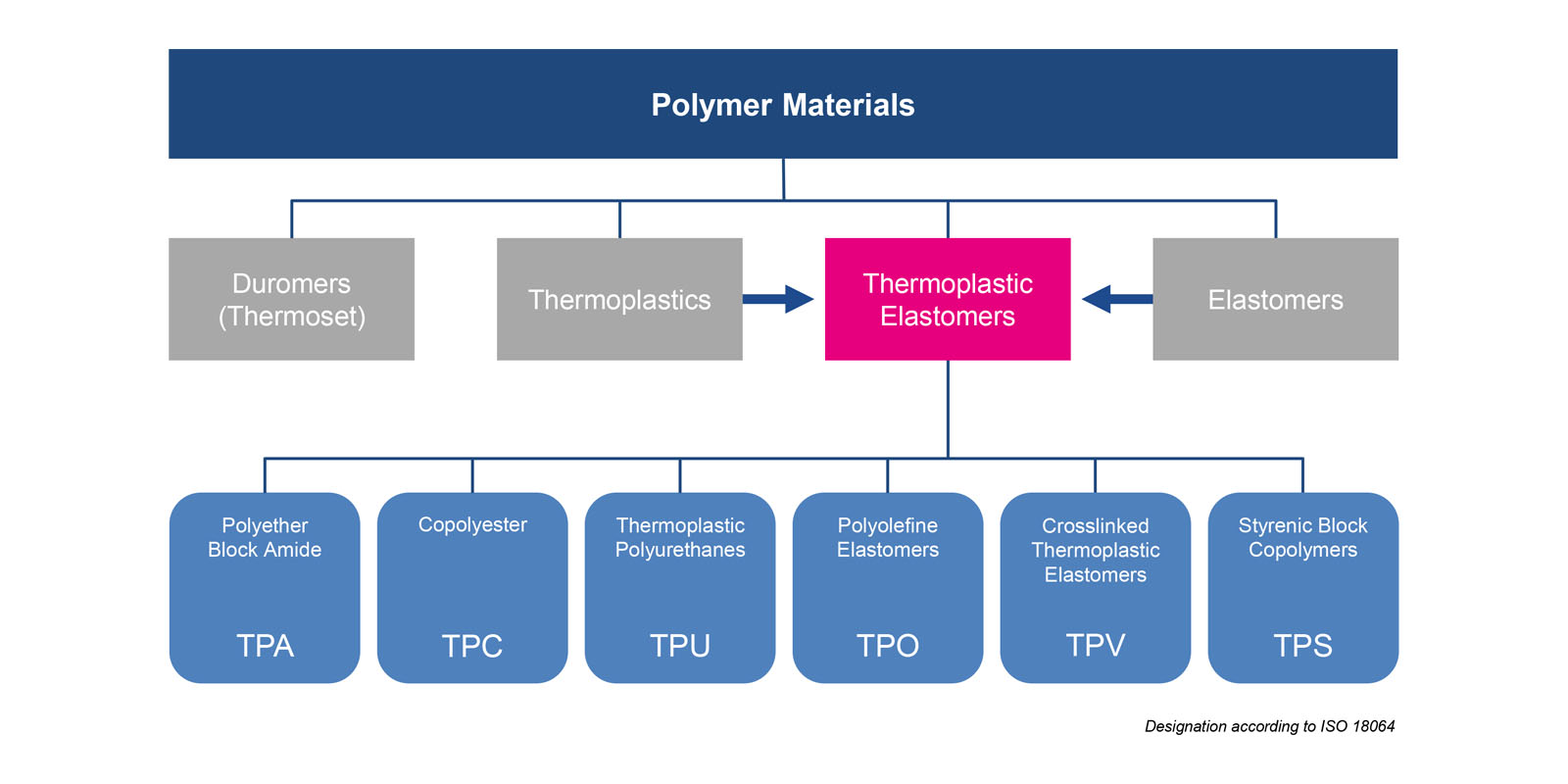
What are Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)?
TPE - Thermoplastic elastomers are an indispensable tool used by processors, product developers and designers alike. They combine the dynamic processing properties of thermoplastic plastics with the softness and flexibility of elastomers.
The different types of TPE
The different types of TPEs and their modification options provide the basis for plenty of materials properties thus enabling a cost-effective processing in applications for the most diverse industries.
TPEs contribute to enhancing products and setting them apart from others. In addition, they take over a lot of technical functions that so far have been reserved for elastomers. Using TPEs does not only increase a product’s benefits but also brings economic advantages to processors.
The processing and behavior of TPE materials classify them as belonging to a group of materials between thermoplastics and elastomers. They form an independent class of materials.
Basically, a distinction is made between reactor-made TPEs (e.g. TPA, TPU, and TPC) and TPE compounds (e.g. TPS and TPV). The properties of reactor-made TPEs are implemented in one polymer. The properties of TPE blends result from mixing different polymers to form a so-called compound.
How is TPE processed?
Like thermoplastics, TPEs are heated to process them by means of injection molding or extrusion. As they show their original elastic properties again after cooling down, they are recyclable like thermoplastics. In contrast to TPEs, elastomers cannot be processed by melting; they are chemically crosslinked and not recyclable.
What are the strongest arguments in favor of using TPE?
- Easy thermoplastic processing
- Short cycle times
- Low energy consumption
- Multi-component processing and thus reduced assembly costs
- Combination of different materials (e.g. hard-soft composite)
- 100% recyclable in processing
- A wide processing window
- Plenty of coloring options, including color effects for more design flexibility
- Many possible applications ranging from the automotive sector to the pharmaceutical industry.

